Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Recent studies demonstrated that current European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society spirometric reference equations, used in general population, may not be applicable in population of elite athletes. Althought it is well known that physical activity may affect lung volumes, the effect of sporting activity on pulmonary function testing indices was never examined. The aim of this study was to examine the differences in functional respiratory parameters in various types of sports by measuring lung volumes and to extend the existing factors as well as sport disciplines which affect respiratory function the most.
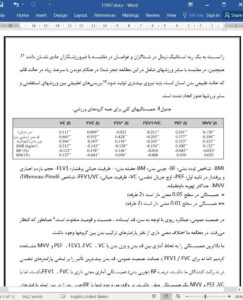
SUBJECTS AND METHODS: A total of 1639 elite male athletes, aged 18-35 years were divided in 4 groups according to the predominant characteristics of training: skill, power, mixed and endurance athletes. They performed basic anthropometric measurements and spirometry. Groups were compared, and Pearson’s simple correlation was performed to test the relation between anthropometric and spirometric characteristics of athletes.
RESULTS: All anthropometric characteristics significantly differed among groups and correlate with respiratory parameters. The highest correlation was found for body height and weight.
CONCLUSIONS: Sports participation is associated with respiratory adaptation, and the extent of adaptation depends on type of activity. Endurance sports athletes have higher lung volumes in comparison with skill, mixed and power group of sport.
Study perspectives: The study was conducted on a large sample size of athletes who perform wide range of different type of sport. The fact that inspiratory muscle fatigue occurs during sport activity provides further challenge to investigate the potential role of respiratory muscles training as a method to enhance physical performance. Clear patterns of the sport that shows the most obtains or the most efficacious training protocol of inspiratory/respiratory muscle training are more difficult to perceive. Rowing and canoeing, swimming, long-distance running and marathon, cycling, triathlon and pentathlon are the sports which improve respiratory system the most.