Abstract
F Face recognition has been widely used in modern intelligent systems, such as smart video surveillance, online payment, and intelligent access control system. Existing face recognition algorithms are prone to be attacked by various face presentation attacks (face-PAs), such as printed paper, video replay, and silicone masks. To optimally handle the aforementioned problems, we formulate a novel deep architecture to increase the accuracy of multi-view human face recognition. In particular, in the first place, a novel deep neural network is built for deeply encoding the face regions, where a novel face alignment algorithm is employed to localize the key points inside faces. Subsequently, we utilize the well-known PCA for reducing the dimensionality of the deep features and simultaneously, removing the redundant and contaminated visual features. Thereafter, we propose a joint Bayesian framework in order to evaluate the similarity of feature vectors and highly competitive face classification accuracy can be achieved. Comprehensive experiments were conducted on our compiled CAS-PEAL dataset and achieved a 98.52% face recognition performance. Moreover, our proposed face recognition system can robustly handle various face recognition attack under various contexts.
1. Introduction
In recent years, face recognition has attracted lots of attention in plenty of domains. The relevant techniques can be employed in different intelligent systems, for example, smart phone unlocking, online payment and access control system [1–3]. The objective of face recognition is to localize/detect and track various human faces by leveraging the captured images. This technique plays a highly important role in biological verification. Each face recognition system captures a face image from one or multiple persons by utilizing a camera, and thereafter it compares the human face with the face samples that are already fed into the face database to fulfill the recognition. Face recognition exhibits the feature of non-contact, wherein it may not be descriptive for the identified person to deliberately join the feature collection. In this way, the output of rejecting the identified person will be identified. In this way, human face recognition technology is highly useful to biometric identification domain.
5. Conclusions
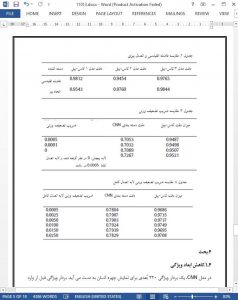
A face image recognition algorithm based on deep neural network is proposed. It includes the use of convolutional neural network to extract facial features, the use of PCA algorithm for feature dimensionality reduction, and the use of joint Bayesian method for vector similarity judgment. Finally, the purpose of improving the accuracy of face image recognition is achieved. After a series of experimental comparisons, the results show that on the CAS-PEAL data set, the accuracy of face image recognition can reach 98.52%.