Abstract
Reactive power generation has been commonly used for power loss minimization and voltage profile improvement in power systems. However, the opportunity cost of reactive power generation should be considered since it affects the frequency control capability of the generator to some degree. This paper proposed a distributed nonlinear control based algorithm to achieve the optimal reactive power generation for multiple generators in a power grid. The reactive power control setting update for each generator only requires local measurement and information exchange with its neighboring buses. It is demonstrated that the proposed algorithm can reduce the non-convex objective function monotonically till convergence and achieve comparable solutions to the centralized technique: particle swarm optimization with faster convergence speed. The proposed algorithm has been tested on the IEEE 9-bus, 39-bus and 162-bus systems to validate its effectiveness and scalability.
Introduction
Reactive power generation has been widely used to improve the voltage of the buses as well as minimize the power loss in the conventional power systems. Abundant control and optimization techniques have been developed for the optimal reactive power control such as linear programming [1], gradient method [2], interior point method [3,4], and sequential quadratic programming algorithm [5]. Shortcomings of these solutions include sensitivity to initial conditions and mathematical restriction on objective functions, such as convexity. Recently, numerous computational intelligent based methods have been proposed to overcome the shortcomings of the traditional algorithms such as, Gravitational Search Algorithm [6], Differential Evolution Algorithm [7], Enhanced Genetic Algorithm [8], Artificial Bee Colony [9], and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [10]. However, all these algorithms require sophisticated communication network for global information collection and are usually implemented offline in a centralized way.
Conclusions
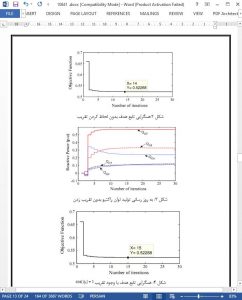
This paper proposed a distributed nonlinear control based algorithm for optimal reactive power control of multiple generators in a power grid. Active power loss, voltage deviation and reactive power generation cost are taken into consideration, and the optimal reactive power control of multiple generators is formulized as a non-convex problem. Only information exchange among neighboring buses is used to achieve the optimal solution, thus, the computational and communication burden are reduced compared to centralized algorithms. It has been demonstrated that by approximating cos(dji) = 1, the calculation for online application is simplified and can still provide comparable results to that of the one without approximation at normal level of generation/load condition. The effectiveness of the proposed distributed nonlinear control based algorithm is validated by comparing to the centralized algorithm: PSO, for IEEE 9-bus, 39-bus and 162-bus systems.