Abstract
Purpose This paper aims to examine the compliance of disclosure with the financial accounting standards of the Accounting and Auditing Organisation for Islamic Financial Institutions’ (AAOIFI) related to Islamic financing products by Islamic banks in Bahrain and Qatar.
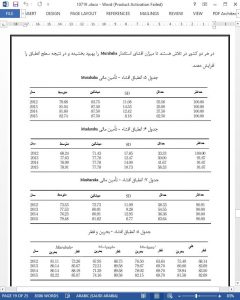
Design/methodology/approach The study measures compliance using disclosure indexes. The disclosure indexes include the three financial accounting standards of Murabaha, Mudaraba and Musharaka. The data are collected from the annual reports of 24 Islamic banks in Bahrain and Qatar over a period of 2012-2015.
Findings The paper found that Islamic banks in Bahrain and Qatar comply with AAOIFI financial accounting standards related to Murabaha, Mudaraba and Musharaka. However, there was a level of non-compliance in both countries. In addition, it found that the extent of compliance had increased over the 2012-2015 period. Also, the Murabaha standard had the highest mean of compliance. Moreover, the results showed that the Islamic banks in Qatar tend to have more compliance of overall Murabaha and Mudaraba disclosures compared to the Islamic banks in Bahrain.
Research limitations/implications The findings are preliminary and highlight that the issue is of high interest to Islamic banks and AAOIFI. Hence, it requires a detailed follow-up to form a complete picture that would assist AAOIFI and regulators gear their policies toward better quality disclosure by Islamic financial institutions. Even though the findings are encouraging, future research is recommended to enforce compliance with the AAOIFI financial accounting standards.
Originality/value This is a pioneer empirical study that focuses on the level and trend of compliance with AAOIFI financial accounting standards related to the Islamic financing products of Murabaha, Mudaraba and Musharaka standards, especially in Qatar. Additionally, it is the first study comparing between the only two Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, i.e. Bahrain and Qatar, that mandatory apply the AAOIFI standards.
1. Introduction
The Islamic financial system differs from the conventional banking system due to its application of Islamic Shari’ah rules (i.e. Islamic law). The teachings of Islam prohibit products that charge riba (i.e. interest or usury) which conventional banks apply as a cost of advancing credit. In contrast, Islamic finance is based on the idea of profit-risk sharing. Under this model, the Islamic bank undertakes to share profits derived from an investment by a customer as well as potential losses arising from the venture. Islamic banking is continuing its tremendous expansion across the globe with assets reaching up to $1.3tn. After the establishment of the first Islamic bank in Dubai in 1975, Islamic banking increased rapidly and with more than 300 banks spread across more than 70 countries. A large portion of these Islamic banks is located in countries comprising the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). The increased expansion has led to the need to establish a regulatory framework to oversee their operations and handle the task of preparing useful standards. To this end, the Accounting and Auditing Organisation for Islamic Financial Institutions (AAOIFI) was established in 1991 to prepare accounting, auditing, governance, ethics and Shari’ah standards for Islamic Financial Institutions (IFI). However, little research has investigated the compliance with such standards.
5. Conclusion
Islamic banking recently showed a rapid increase all over the world, especially and in the GCC countries. The AAOIFI standards came into being to fill the gap by providing accounting standards that evaluate the main needs of the IFIs. The current study aimed to examine the extent and trend of compliance of disclosure with the AAOIFI financial accounting standards requirements of Murabaha (FAS2), Mudaraba (FAS3) and Musharaka (FAS4) by Islamic banks in Bahrain and Qatar over the 2012-2015 period. The study found the compliance of disclosure of the AAOIFI Murabaha, Mudaraba and Musharaka financial accounting standards by Islamic banks in Bahrain and Qatar was relatively high over the period 2012-2015. However, the Islamic banks in both countries were not fully complied with almost a mean of 20. This finding indicates that there is a gap in the compliance with some particular requirements which need to be further assessed by the Islamic banks and central banks in both countries on the one side and AAOIFI in the other