Abstract
Digital transformation of manufacturing is a hot topic among strategic managers of manufacturing companies. The crux of digital transformation lies in the digitalization of manufacturing supply chain (MSC). However, the digital transformation of the MSC is highly uncertain, owing to the dynamic and complex changes of its nodes and structure in response to growing customer demand and fierce market competition. To propel the MSC digital transformation, it is crucial to effectively identify and predict the risk factors in the course of digital transformation. Therefore, this paper attempts to help manufacturing companies in China to successfully switch to a digital MSC. Firstly, the risk sources of the MSC digitization were identified, and complied into an evaluation index system for the digital transformation of the MSC. Next, the principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to reduce the dimension of the original data by revealing the three key principal components, and then the characteristic parameters of risk prediction are selected, so as to simplify the structure of neural network and improve the speed and efficiency of network training. On this basis, a backpropagation neural network (BPNN) was constructed for predicting the risks in MSC digitization. The results of training the model based on some data show that the proposed BPNN model has a good predictive effect. Furthermore, our model was compared with the traditional artificial neural network (ANN) model on a test set. The comparison demonstrates that our model achieved better effect than the traditional model in risk prediction. The results also show that the selected three principal components are reasonable, and the evaluation index system is valuable. The research results provide new insights to the smooth digital transformation of the MSC.
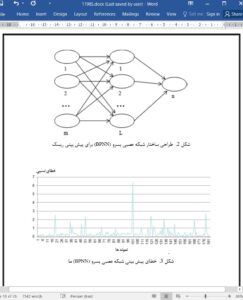
7. Conclusions
The digital transformation of China’s manufacturing is a new phenomenon, with no experience to learn from. Many traditional manufacturing companies in China are faced with great difficulties in quickly completing the digital transformation, partly owing to the numerous uncertainties and risks that arise in the course of the transformation. For the smooth implementation of digital transformation among manufacturing companies in China, this paper identifies the risk factors of traditional manufacturing companies in digital transformation, referring to the relevant literature, and compiles them into an evaluation index system. Next, the PCA was carried out to extract the principal risk factors of digital transformation based on the survey data, and used to train and improve the BPNN risk prediction model. Simulation results show that the proposed BPNN prediction model is very useful. The risk composition is reasonable. Among the three key principal components, the weak strategy consistency is the most significant factor. This factor not only undermines the stability of the digital SC, but also affects the operating environment and weakens the risk management ability of companies. The follow-up research will further improve our prediction model. For example, the size, diversity, and quality of samples will be increased; the evaluation index system will be verified through even more tests, and adjusted to enhance its applicability to real-world scenarios.