Abstract
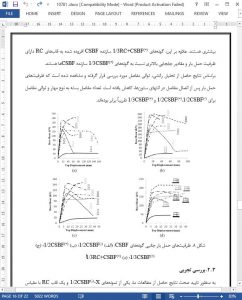
There are many studies in the literature conducted on the subject of ensuring earthquake safety of reinforced concrete and steel structures using steel braced frames, but no detailed study concerning individual behavior of steel braced frames under earthquake loads and strengthening of reinforced concrete structures with outof-plane steel braced frames has been encountered. In this study, in order to evaluate behaviors of “Concentrically Steel Braced Frames” types defined in TEC-2007 under lateral loads, dimensional analysis of Concentrically Steel Braced Frames designed with different scales and dimensions was conducted, the results were controlled according to TEC-2007, and after conducting static pushover analysis, behavior and load capacity of the Concentrically Steel Braced Frames and hinges sequence of the elements constituting the Concentrically Steel Braced Frames were tested. Concentrically Steel Braced Frames that were tested analytically consist of 2 storey and one bay, and are formed as two groups with the scales 1/2 and 1/3. In the study, Concentrically Steel Braced Frames described in TEC-2007 were designed, which are 7 types in total being non-braced, X-braced, V- braced, Λ- braced, \- braced, /- braced and K- braced. Furthermore, in order to verify accuracy of the analytic studies performed, the 1/2 scaled concentrically steel X-braced frame test element made up of box profiles and 1/3 scaled reinforced concrete frame with insufficient earthquake resistance were tested individually under lateral loads, and test results were compared with the results derived from analytic studies and interpreted. Similar results were obtained from both experimental studies and pushover analyses. According to pushover analysis results, load-carrying capacity of 1/3 scaled reinforced concrete frames increased up to 7,01 times as compared to the non-braced specimen upon strengthening. Results acquired from the study revealed that reinforced concrete buildings which have inadequate seismic capacity can be strengthened quickly, easily and economically by this method without evacuating them.
1. Introduction The lateral load-carrying capacity, strength and stiffness of a building might be increased by shear walls used in the system. These shear walls may be either reinforced concrete (RC) or made of “Concentrically Steel Braced Frames (CSBF)” indicated in (TEC2007). Steel braced frames are systems constituting of hinged joint or moment resisting frames and braced bound to these frames as centric and eccentric.
4. Conclusions
Experimental studies and pushover analyses revealed similar results for the analyzed systems throughout this study. The load carrying capacity of RC frames with inadequate earthquake resistance were increased significantly by adding CSBFs. Specimens designed in accordance with TEC-2007 have more load-carrying capacities compared to those that are not designed conveniently with TEC-2007 (2007). The specimens having different scales (1/2 and 1/3) revealed similar behavior. One of the most significant findings of the study is that, structures can be strengthened by the suggested method, without complete evacuation and/or partial closure. For buildings to be strengthened via this technique, it is primarily suggested to add foundations outside of buildings, and connect them rigidly between each other and also with the main structure. Additionally, strengthening of RC buildings with Λ- braced and X braced gives better results in terms of ductility, energy consumption capacity and load-carrying capacity. Therefore, using Λbrace and X brace is recommended for strengthening with CSBF.
In the light of these results, it was concluded that the seismically deficient RC frames can be strengthened by adding external concentric steel braced shear walls rapidly, easily and economically. Another advantage of this method is that, the structure can be strengthened without destroying the plasters, paintings and other finishings.