Abstract
Image identification is becoming a crucial step in most of the modern world problem-solving systems. Approaches for image detection, analysis and classification are available in glut, but the difference between such approaches is still arcane. It essential that proper distinctions between such techniques should be interpreted and they should be analyzed. Standard American Sign Language (ASL) images of a person’s hand photographed under several different environmental conditions are taken as the dataset. The main aim is to recognize and classify such hand gestures to their correct meaning with the maximum accuracy possible. A novel approach for the same has been proposed and some other widely popular models have compared with it. The different preprocessing techniques used are Histogram of Gradients, Principal Component Analysis, Local Binary Patterns. The novel model is made using canny edge detection, ORB and bag of word technique. The preprocessed data is passed through several classifiers (Random Forests, Support Vector Machines, Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression, K-Nearest Neighbours, Multilayer Perceptron) to draw effective results. The accuracy of the new models has been found significantly higher than the existing model.
1. Introduction
Understanding sign language is an arduous task and it is a skill that has to be learned with practice. But with this paper, we aim to provide several schemes of identifying and understanding such letters without learning the sign language. We focus primarily on the development of new procedures to understand sign language, and to find differences between the approaches and best method of recognition of the sign language. There are several difficulties in developing a better method for sign recognition such as, in real life the images captured are so excessively noisy that high level of pre-processing is required, the datasets available online are generally so noiseless, that working on them leads to the development of models trained only to handle images with less or nearly no noise, hence being impractical for real-life application. Thus, it is imperative to create a model that can handle noisy images and also be able to produce positive results.
Conclusion and Future
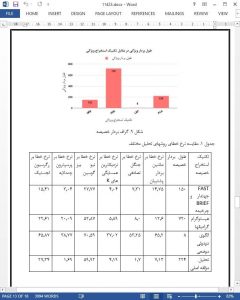
ScopeIn the presented paper, the proposed technique of ORB feature extraction has been tested against many different pre-processing techniques such as Histogram of Gradients, LBP and PCA on the same dataset. These approaches have been successfully passed through various prominent classifiers such as KNN, SVM, Random Forest, Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression and Multi-Layer Perceptron. The proposed technique outperforms all the other pre-processing techniques for Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression and KNN classifiers while PCA outperforms all the other techniques for MLP, Random Forest and SVM classifiers. Although the approach gives substantially high accuracy for recognition of gestures.