Abstract
Wireless Network-on-Chip (WNoC) architectures are introduced to improve performance by reducing the core-to-core communication latency. Conventional WNoCs broadcast messages that increase bandwidth-traffic, communication delay, and power consumption. Studies show that directory-based architectures have potential to address message broadcasting and improve performance. This work proposes a novel WNoC architecture with distributed directories (WNoC-DDs) that supports wireless communications to enhance faster execution by reducing latency. VisualSim software package is used to model and simulate the proposed WNoC-DDs, a WNoC with centralized directory (WNoC-CD), and a traditional 2D mesh by processing different communication scenarios. The proposed architecture helps reduce the total hop count and unwanted broadcasting among nodes in a WNoC-DDs. Experimental results show that the proposed WNoC-DDs reduces communication delay up to 20.54% and 5.40%, respectively, when compared to mesh and WNoC-CD. Similarly, the proposed WNoC-DDs reduces power consumption up to 73.56% and 19.97%, respectively, when compared to mesh and WNoC-CD.
1. Introduction
The dominant technology such as Network-on-Chip (NoC) is becoming trendy and can solve performance limitations of traditional wired interconnects and productive for System-on-Chip (SoC) architectures. Recent studies indicate that lot of products, such as, processors, cell phones, memory subsystems and many other embedded products are integrated on a single chip and interconnected by NoC [1–3]. The design of multicore systems makes easy to solve complex jobs by working concurrently in parallel with improved execution speed and reduced power consumption [4,5]. Multithreading is a process in which a central processing unit (CPU) can execute several number of threads simultaneously. Memory-balanced scheduling is a thread scheduling approach that improves the performance by balancing memory access requirements but at the cost of interconnects width and bandwidth [6].
6. Conclusions
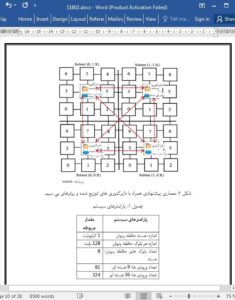
Performance of modern Network-on-Chip architectures depends on communication latency, hop count, and power consumption. If the communication setup-time is quick, then the system performance should be better. In this work, we introduce a WNoC architecture with distributed directories (WNoC-DDs) to improve the performance to power ratio. A directory allows the tasks to execute faster by providing adaptive minimal routing path to reach the destination node. VisualSim Architect is used to model and simulate the architectures by using synthetic workload.